
The error function erf(x) (integral of probability), Hyperbolic cosecant csch(x), hyperbolic arcsecant asech(x), Secant sec(x), cosecant csc(x), arcsecant asec(x),Īrccosecant acsc(x), hyperbolic secant sech(x), Other trigonometry and hyperbolic functions: The equation solver allows to solve equations with an unknown with calculation steps : linear equation, quadratic equation, logarithmic equation, differential equation. Hyperbolic arctangent atanh(x), hyperbolic arccotangent acoth(x) Just like on the Systems of Linear Equations page.

Hyperbolic arcsine asinh(x), hyperbolic arccosinus acosh(x), Using the Matrix Calculator we get this: (I left the 1/determinant outside the matrix to make the numbers simpler) Then multiply A-1 by B (we can use the Matrix Calculator again): And we are done The solution is: x 5, y 3, z 2. Hyperbolic tangent and cotangent tanh(x), ctanh(x) Hyperbolic sine sh(x), hyperbolic cosine ch(x), Sinus sin(x), cosine cos(x), tangent tan(x), cotangent ctan(x)Įxponential functions and exponents exp(x)Īrcsine asin(x), arccosine acos(x), arctangent atan(x), y-terms are opposites, you do not need to multiply either equation by a constant. Solve the system of linear equations by elimination. There are three methods typically used to solve systems of linear equations: graphing, the. Most of the systems of equations you see in algebra are sets of two linear equations in the standard form Ax + By C. The modulus or absolute value: absolute(x) or |x| Students will be able to solve a system of linear equations by elimination. Systems of equations are sets of equations where the solution is the intersecting point (s) between the equations.

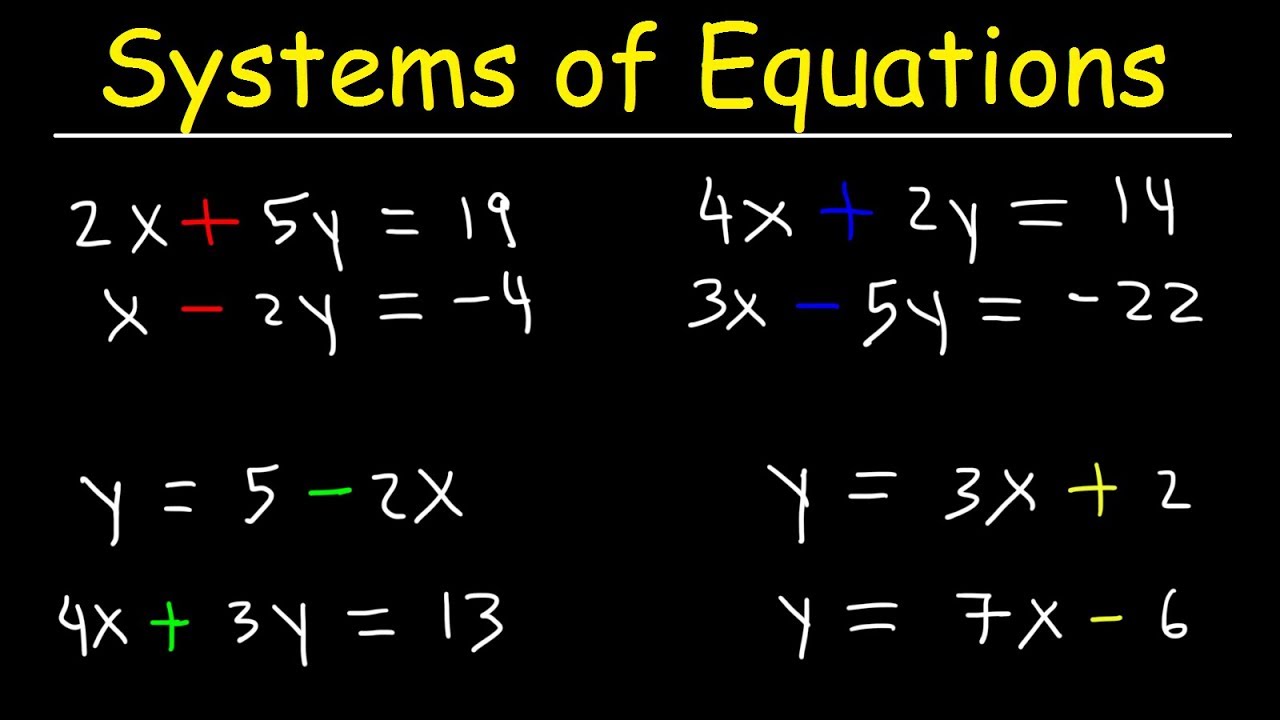
A system of three equations with three variables.A system of two equations with two unknowns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
